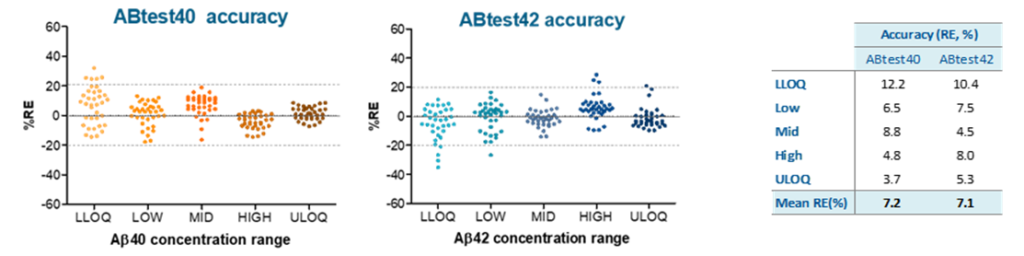
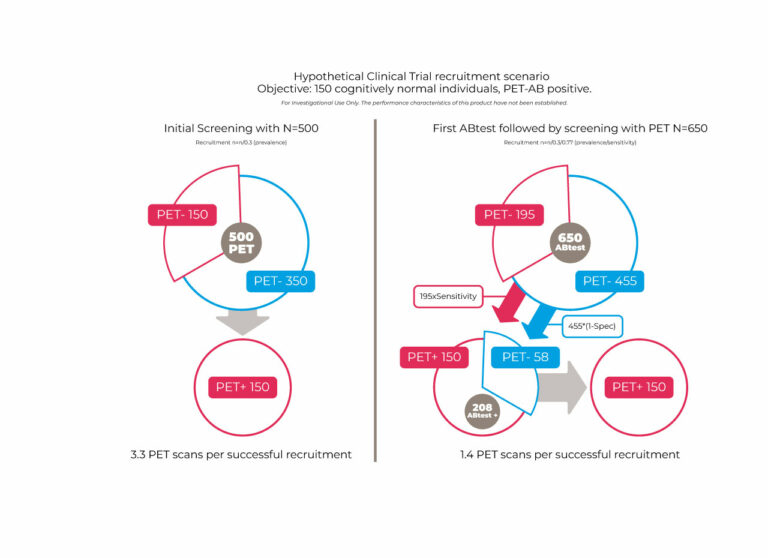
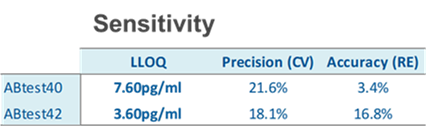
The table shows the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) determined in accordance with EMA and FDA recommendations. These levels are well below the average levels detected in healthy people and patients with AD.
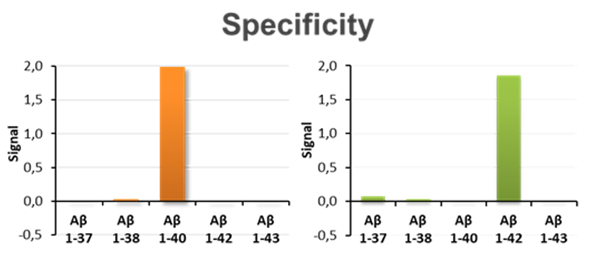
The chart shows the specificity of Aβ40 and Aβ42 determinations characterised by the almost complete absence of cross-reactivity with other peptides similar to each of the target peptides.